Healthy Boost
What’s the problem and Healthy Boost solution?
The project addressed the transnational challenge of the health burden due to unhealthy lifestyles of the city residents, which cannot be solved by the current fragmented, incoherent urban policies. The project wanted to contribute to the improved – more innovative, effective and integrated – cross-sectoral urban policies. Healthy Boost enabled the participation of citizens in planning policies for health and wellbeing and improved cross-sectoral cooperation in cities of the Baltic Sea region to support cities´ administrations in the provision of health services. In addition, the project enhanced the innovativeness of the administrations in the Baltic Sea region to respond better to current and future complex challenges in the municipalities.
What will stay after the project is over?
The Healthy Boost project brought together fourteen partners representing different levels of governance within various sectors. The main objective of the project was to make urban policies for health and well-being more innovative, more effective and more integrated. The main output of Healthy Boost project was a model for effective cooperation for cross-sectoral urban policies for health and wellbeing developed and tested by nine cities in six countries. Improved after the feedback from different stakeholders, it shall serve other cities in more integrated future work.
Budgets
in numbers
-
2.54MillionTotal
-
1.90MillionErdf
-
0.15MillionEni + Russia
-
0.00MillionNorway
Achievements
How did it all started?
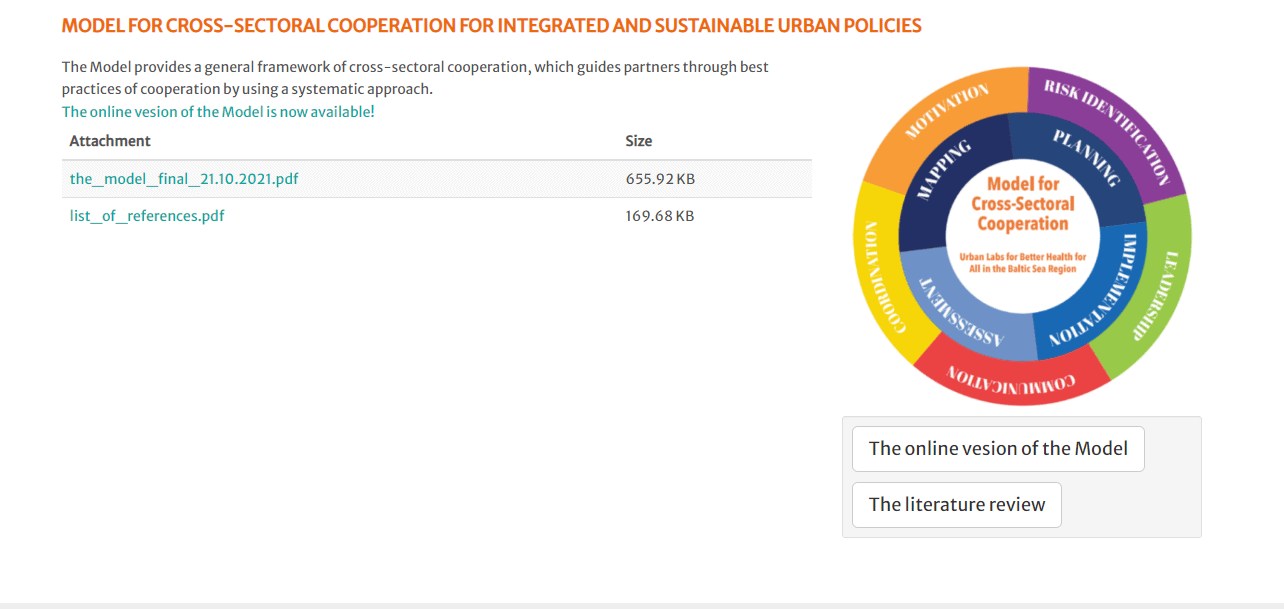
The project developed a model for cross-sectoral cooperation for health promotion. It was based on scientific literature research and complemented by a self- assessment in the partner cities of Poznan, Klaipeda, Jelgava, Tartu and Turku. The self-assessment gave information of a city’s institutional capacity to implement cross-sectoral cooperation from two points of view: the formal structures for the cooperation (strategies, processes, practices) and the way cooperation works. The project identified gaps in five strategic and operational domains of cooperation: risk identification, leadership, communication, coordination, motivation. After the model was completed, the partner cities ran several pilots along the lines of the specific roadmaps that the city partners designed beforehand (to set scope, timing, goals, actors).
First benefits from cross-sectoral cooperation.
All pilots addressed the need for more effective cooperation for cross-sectoral urban policies for health and wellbeing. Even if the need and the model were the same, the pilots were different. One pilot addressed, for instance, the problem of residents’ physical inactivity, while another was about the need for healthier food in schools and children´s better-eating habits. One pilot focused on the lack of space for physical exercise, another was centered on the communication about health and wellbeing services. The following cities successfully run the pilots and started benefitting from applying cross-sectoral cooperation: Tartu (EE), Helsinki and Turku (FI), Klaipeda (LT), Jelgava (LV), Poznan and Suwalki (PL), Cherepovets and Pskov (RU). City employees worked together with citizens (children, adults, elders) and NGOs. For instance, in Jelgava the pilot focused on healthy, local and sustainable food from the early childhood and school years. The pilot engaged around 200 children, who improved their eating habits in schools, and as a cascading effect, their families benefited too.
Outputs
Self-assessment tool and matrix for cities.

Model for cross-sectoral cooperation for integrated and sustainable urban policies.
Project Stories
Partners
City of Turku
- TownTurku
- RegionVarsinais-Suomi
- CountryFinland
- RepresentativeMaarit Luukkaa
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Metropolia University of Applied Sciences
- TownHelsinki
- RegionHelsinki-Uusimaa
- CountryFinland
- RepresentativeArja Liinamo
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
SUCCEEDED by PP01 (01.03.2019) Baltic Region Healthy Cities Association
- TownTurku
- RegionVarsinais-Suomi
- CountryFinland
- RepresentativeMaarit Luukkaa
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Lithuanian University of Health Sciences
- TownKaunas
- RegionKauno apskritis
- CountryLithuania
- RepresentativeAgnė Slapšinskaitė
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Jelgava Local Municipality
- TownJelgava
- RegionRīga
- CountryLatvia
- RepresentativeAnita Skutane
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Riga Stradiņš University
- TownRiga
- RegionRīga
- CountryLatvia
- RepresentativeAnita Villeruša
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
City of Poznań
- TownPoznań
- RegionMiasto Poznań
- CountryPoland
- RepresentativeZuzanna Kwiatkowska
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Suwalki Municipality
- TownSUWAŁKI
- RegionSuwalski
- CountryPoland
- RepresentativeEmil Sieńko
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Nofer Institute of Occupational Medicine
- TownLodz
- RegionMiasto Łódź
- CountryPoland
- RepresentativePiotr Sakowski
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Västerbotten County Council
- TownUm eå
- RegionVästerbottens län
- CountrySweden
- RepresentativeAnna Nordström
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Association "Healthy cities, districts and villages"
- TownCherepovets
- RegionVologda Oblast
- Country
- RepresentativeTatiana Shestakova
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Science Park Tehnopol
- TownTallinn
- RegionPõhja-Eesti
- CountryEstonia
- RepresentativePiret Hirv
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Tartu City Government
- TownTartu
- RegionLääne-Eesti
- CountryEstonia
- RepresentativePiret Väljaots
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
City of Helsinki
- TownHelsinki
- RegionHelsinki-Uusimaa
- CountryFinland
- RepresentativeMinna Kaattari
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Klaipeda City Public Health Bureau
- TownKlaipeda
- RegionKlaipėdos apskritis
- CountryLithuania
- RepresentativeLaura Kubiliutė
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
-
Project managerAdham MaharramliCity of Turku
-
Legal representativeBjörn GrönholmCity of Turku
-
Financial managerJussi VälimäkiCity of Turku
-
Communication managerLaura LuukkonenCity of Turku