DAIMON 2
Legacy at the bottom of the Baltic Sea
Some 50,000 tons of chemical munitions and 200,000 tons of conventional munitions were dumped into the Baltic Sea after World Wars I and II. So far, there have been no efforts to remove the dangerous legacy from the bottom of the Baltic Sea. However, the recently increasing construction of pipelines, cables and wind farms at sea as well as natural corrosion of dumped containers increase the risk of explosions near populated areas and of contamination of the environment.
Over the years, there was an ongoing discussion on how to assess and manage the environmental risk of dumped ammunition. Although the environmental effects of some of harmful substances, such as arsenic compounds, are well known, in other cases, the knowledge is insufficient to make proper risk assessments.
Thanks to the DAIMON project, maritime administrators and spatial planners, environmental agencies, coastguards and military are more aware of the risk. However, they do not sufficiently use newly developed tools for risk analysis, selection of remediation methods as well as environmental impacts assessment. The DAIMON 2 offers training in using the new tools and develops them further into standard operating procedures for the environmental impact assessment.
Budgets
in numbers
-
0.90MillionTotal
-
0.66MillionErdf
-
0.00MillionEni + Russia
-
0.03MillionNorway
Achievements
With the access to the tools developed by the preceding project DAIMON, the partner organisations of DAIMON 2 focused on the practical implementation of the tools and their further optimisation.
Decision support system improved
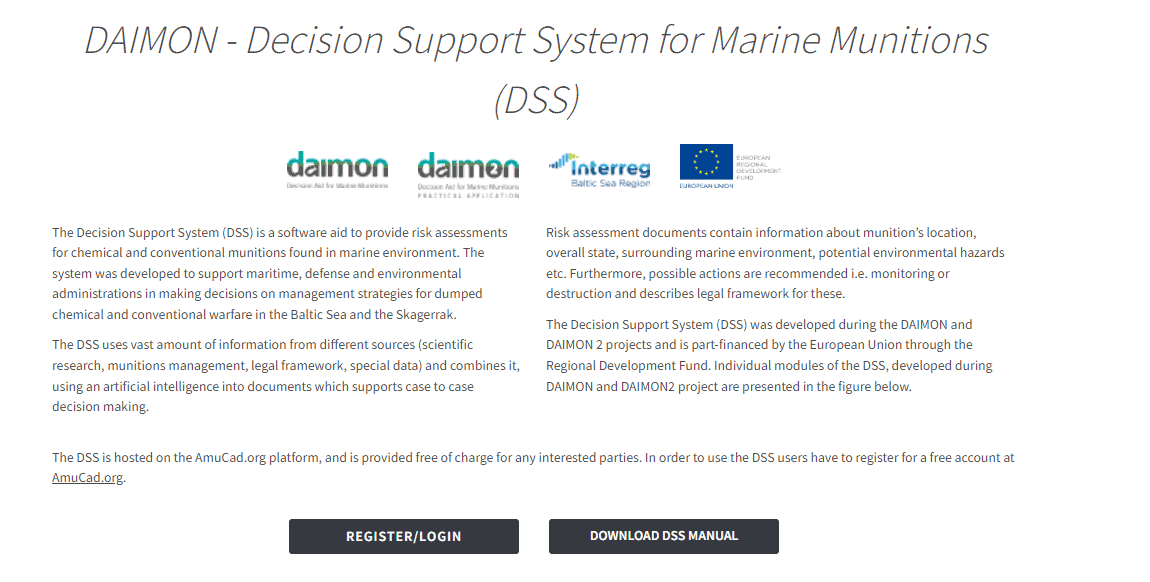
The DAIMON 2 partners optimised the previously developed decision support system (DSS) for marine chemical and conventional munitions. Such parameters as user experience, performance and understanding of the suggested by the system reports constitute the basis for optimisation of the tool. Thanks to optimisation, the software system contains recommendations in regard to the needed procedures based on the performed risk analysis. In addition, it suggests management strategies to improve the situation assessed by the tool through risk categorisation. Furthermore, the partners finalised the integration of the risk assessment model into the decision support system. The DSS received an upgrade in terms of durability and extended use, being embedded into the Ammunition Cadastre Sea platform (AmuCad.org) and is available for all interested users free of charge.
Besides, the partners organised training on DSS and integrated the received feedback, recommendations and comments to the system. In addition, the participating organisations conducted webinars dedicated to EcoTox toolbox training and the e-learning platform/online tutorial.
The training targeted e.g. environmental agencies, maritime administrations, military, spatial planning, coastguards and offshore investors. The training reached out to more than 200 participants.
Environmental impact assessment procedures included into the decision support system
The DAIMON 2 partners developed 33 Standard/Recommended Operating Procedures (SOPs/ROPs) for environmental impact assessment in offshore areas. The procedures are built on the data from the previously developed EcoTox toolbox factsheets. Besides, the partners introduced new methodologies for detection, impact analysis and monitoring of the dumped conventional and chemical munitions. The methodologies were integrated into the decision support system. Furthermore, standard operating procedures (SOPs) are now considered by the ESPOO convention representatives for possible inclusion as a set of methods in the environmental impact assessment of offshore investment areas with the dumped munition. As an example, the partners presented the standard and recommended operating procedures to offshore companies dealing with building windfarms. The purpose was to raise awareness and consider the inclusion of the methods in the environmental impact assessment of the companies´ investment areas.
Outputs
Optimised decision support system
EcoTox Toolbox training programme

Project Stories
Partners
Institute of Oceanology Polish Academy of Sciences (IOPAN)
- TownSopot
- RegionTrójmiejski
- CountryPoland
- RepresentativeJacek Bełdowski
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Polish Naval Academy (PNA)
- TownGdynia
- RegionTrójmiejski
- CountryPoland
- RepresentativeJacek Fabisiak
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Clausthal University of Technology (TUC)
- TownClausthal-Zellerfeld
- RegionGoslar
- CountryGermany
- RepresentativeMatthias Reuter
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
north.io GmbH
- TownKiel
- RegionKiel, Kreisfreie Stadt
- CountryGermany
- RepresentativeJann Wendt
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
WITHDRAWAL (01/02/2021) Johann Heinrich von Thünen-Institut, Federal Research Institut für Rural Areas, Forestry and Fisheries (TI-FI)
- TownBraunschweig
- RegionBraunschweig, Kreisfreie Stadt
- CountryGermany
- RepresentativeThomas Lang
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
University of Helsinki - VERIFIN
- TownHelsinki
- RegionHelsinki-Uusimaa
- CountryFinland
- RepresentativePaula Vanninen
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Finnish Environment Institute (SYKE)
- TownHelsinki
- RegionHelsinki-Uusimaa
- CountryFinland
- RepresentativeAnu Lastumäki
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Norwegian Defence Research Establishment (FFI)
- TownKjeller
- RegionAkershus
- CountryNorway
- RepresentativeStig-Rune Sellevåg
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
Chalmers University of Technology
- TownGothenburg
- RegionVästra Götalands län
- CountrySweden
- RepresentativeAnders Tengberg
- Phone
- E-Mail
- Web
-
Project managerJacek BeldowskiInstitute of Oceanology Polish Academy of Sciences (IOPAN)
-
Legal representativeJan Marcin WęsławskiInstitute of Oceanology Polish Academy of Sciences (IOPAN)
-
Financial managerJan FidlerBiuro Projektów Fidler
-
Communication managerKatarzyna FidlerBiuro Projektów Fidler