CIRC-2-ZERO Project III Co-Creation Workshop
27 January 2026
CIRC-2-ZERO Project III Co-Creation Workshop on the Development of DTDP Module 2
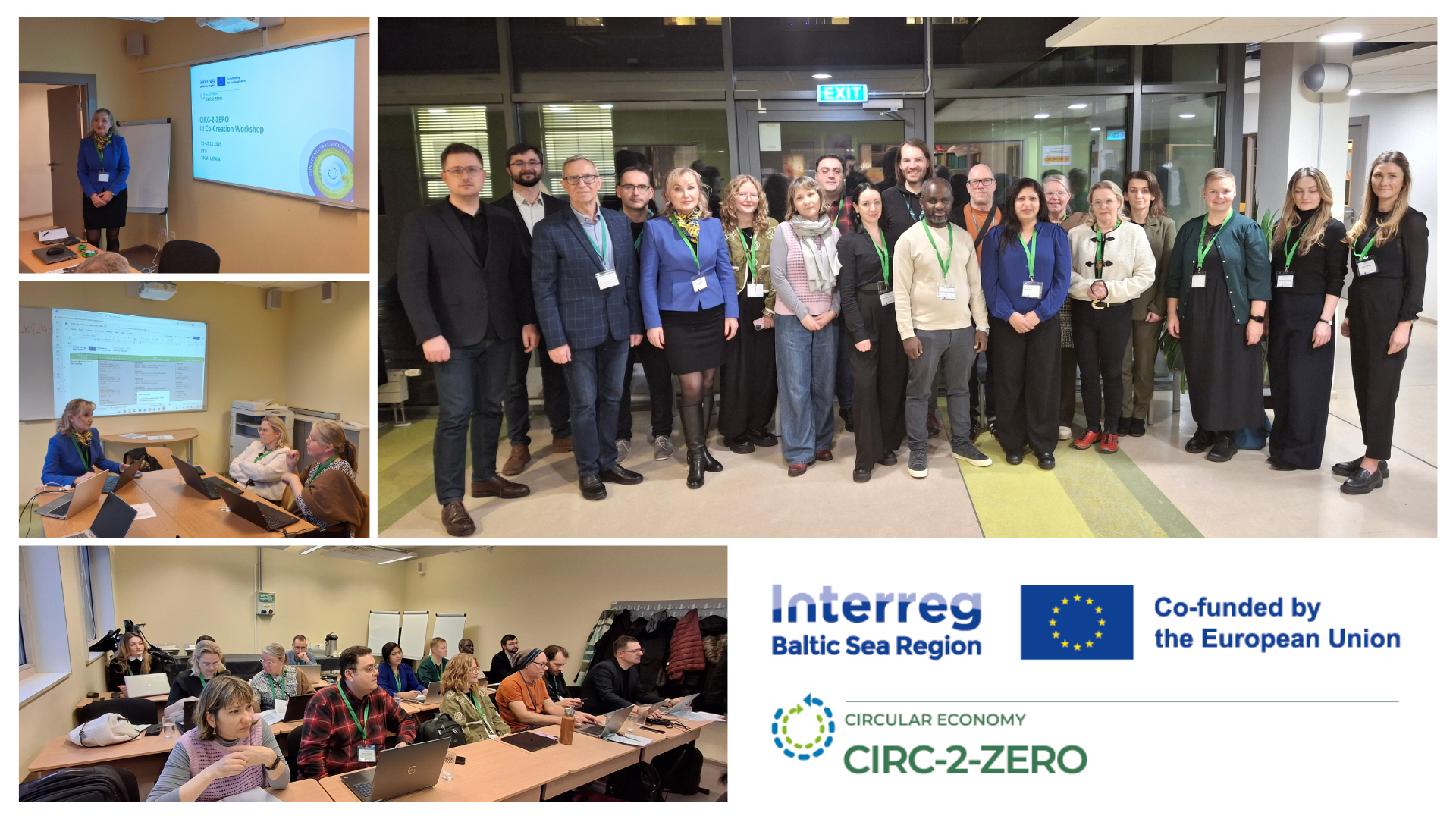
The CIRC-2-ZERO Project successfully conducted its third Co-Creation Workshop 11.-12. December 2025, organised by the project’s lead partner, Häme University of Applied Sciences (HAMK), and hosted by Riga Technical University (RTU). The workshop brought together project partners and industry representatives to jointly address key challenges and opportunities for advancing circular manufacturing practices in the Electronics and Engineered Wood Products (EWP) sectors. The two-day event focused on defining priorities and functional requirements for Module 2 of the project’s Digital Twin Demo Platform.
Workshop Objectives
The workshop was structured around a set of clearly defined objectives, which guided collaborative discussions and hands-on working sessions across both target sectors. Participants aimed to achieve the following objectives:
- identify critical value chain stages and key bottlenecks that currently prevent circularity;
- determine which stages are most impactful for circular economy interventions;
- define indicators to measure circularity performance, including units, data sources and targets; and
- specify how each Module 2 feature should function, including required inputs, expected outputs, visualisation methods and decision-support capabilities.
Day 1: Identifying Value Chain Bottlenecks in Electronics and EWP
The first day of the workshop focused on understanding critical value chain stages and identifying bottlenecks that hinder circular processes for SMEs in the Electronics and EWP sectors. The day began with an overview of the workshop agenda, objectives, and presentations by CIRC-2-ZERO’s company partners, who shared detailed insights into their respective value chains.
VMG Lignum (Lithuania), representing the engineered wood products sector, shared its experience gained through collaboration with international strategic partners. The company manufactures engineered wood products such as laminated veneer lumber (LVL), I-joists, and structural particle boards (P4–P7) for residential, commercial, and public projects, and is also involved in the development of prefabricated building systems. Most core production processes are managed internally – from raw material processing to finished engineered wood products – with adhesives being the only externally sourced component. Strong circular economy practices are an integral part of VMG Lignum’s operations. Approximately 30% of wood waste and packaging materials are reused, including materials sourced from municipal collection points. Production by-products such as wood chips are reused internally for particleboard manufacturing, while wood dust is converted into heat energy to power the factory or supply the local city.
VIZULO (Latvia), representing the Electronics sector, presented a value chain structured around primary and supporting activities. The company specializes in customized lighting solutions for outdoor and indoor applications, including parks, streets, airports, warehouses, and industrial facilities. Supporting activities include human resources, sales management, procurement, supplier management, and R&D, while primary activities cover assembly, testing and quality assurance, packaging, logistics, marketing, and customer support. Due to strict regulatory requirements, VIZULO conducts extensive testing prior to product delivery. At end-of-life, recycling remains challenging due to the complexity of separating materials such as aluminum, electronics, and plastics. However, products are designed for ease of maintenance and repair, and high-quality materials are used to meet demanding market standards.
Following the company presentations, participants worked in smaller groups to map critical value chain stages based on pre-workshop homework and previously collected company data. Groups assessed stages according to material impact, waste generation, and circular potential, and identified specific bottlenecks and root causes, such as business model constraints, design limitations, or organizational challenges. Each country team also identified one to two priority indicators for predefined value chain stages.
The day concluded with a value chain prioritisation exercise, including scoring of stages, identification of the most needed tools, and agreement on which country partners would lead the development of each priority tool.
Day 2: Defining Module 2 Features and Decision-Support Tools
Building on the outcomes of the first day, the second workshop day focused on defining detailed specifications for Module 2 features of the Digital Twin Demo Platform. Participants visualised the equipment manufacturing value chain and highlighted where circular interventions could deliver the greatest impact.
Each group specified how individual Module 2 features should operate, clearly defining:
- inputs – the data entered by users;
- outputs – the information and results generated by the tool;
- display – how information should be visualised; and
- decisions – the key questions the tool is designed to answer.
The tools discussed and further developed included:
- a Value Chain Canvas Tool to visualise the entire value chain and highlight priority areas for circular interventions;
- a Stakeholder Mapper to identify key actors—such as forest suppliers, recyclers, by-product users, and deconstruction partners—and their relationships in the circular transition;
- a Flow Analyzer to track material, energy, water, and by-product flows and identify inefficiencies and circular opportunities, including yield optimisation, by-product valorisation, and cascading;
- a Scenario Simulator to test “what-if” scenarios related to yield improvements, energy investments, by-product valorisation, and cascade strategies; and
- a Best Practice Library providing actionable examples from comparable manufacturers implementing circular economy strategies.